Pregnancy Tips : How to Tell You Are Pregnant
[media id=22 width=500 height=400]
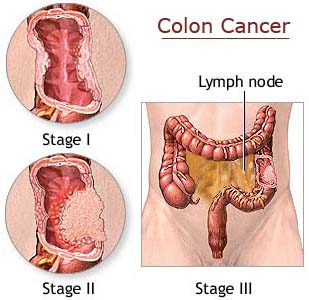
Pregnancy (latin “graviditas”) is the carrying of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, inside the uterus of a female. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets. Human pregnancy is the most studied of all mammalian pregnancies. Obstetrics is the surgical field that studies and cares for high risk pregnancy. Midwifery is the non-surgical field that cares for pregnancy and pregnant women.
Childbirth usually occurs about 38 weeks after conception; i.e., approximately 40 weeks from the last normal menstrual period (LNMP) in humans. The World Health Organization defines normal term for delivery as between 37 weeks and 42 weeks. The calculation of this date involves the assumption of a regular 28-day period.
The best way to determine if a woman is pregnant is by having her blood tested, or she can take a home pregnancy test and look for first trimester symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, headache and hormonal changes. Wait a week after a missed menstrual period to take a pregnancy test with help from a labor and delivery nurse in this free video on pregnancy and obstetrics.
Nutrition
A balanced, nutritious diet is an important aspect of a healthy pregnancy. Eating a healthy diet, balancing carbohydrates, fat, and proteins, and eating a variety of fruits and vegetables, usually ensures good nutrition. Those whose diets are affected by health issues, religious requirements, or ethical beliefs may choose to consult a health professional for specific advice.
Adequate periconceptional folic acid (also called folate or Vitamin B9) intake has been proven to limit fetal neural tube defects, preventing spina bifida, a very serious birth defect. The neural tube develops during the first 28 days of pregnancy, explaining the necessity to guarantee adequate periconceptional folate intake.Folates (from folia, leaf) are abundant in spinach (fresh, frozen, or canned), and are also found in green vegetables, salads, citrus fruit and melon, chickpeas (i.e. in the form of hummus or falafel), and eggs. In the United States and Canada, most wheat products (flour, noodles) are fortified with folic acid.
Weight gain
Caloric intake must be increased, to ensure proper development of the fetus. The amount of weight gained during pregnancy varies among women. The National Health Service recommends that overall weight gain during the 9 month period for women who start pregnancy with normal weight be 10 to 12 kilograms (22–26 lb). During pregnancy, insufficient weight gain can compromise the health of the fetus. Women with fears of weight gain or with eating disorders may choose to work with a health professional, to ensure that pregnancy does not trigger disordered eating. Likewise, excessive weight gain can pose risks to the woman and the fetus. Women who are prone to being overweight may choose to plan a healthy diet and exercise to help moderate the amount of weight gained.
Immune tolerance
The fetus inside a mother may be viewed as an unusually successful allograft, since it genetically differs from the mother. In the same way, many cases of spontaneous abortion may be described in the same way as maternal transplant rejection.
There is substantial evidence for exposure to partner’s semen as prevention for pre-eclampsia, largely due to the absorption of several immune modulating factors present in seminal fluid.
Drugs in pregnancy
Drugs used during pregnancy can have temporary or permanent effects on the fetus. Therefore many physicians would prefer not to prescribe for pregnant women, the major concern being over teratogenicity of the drugs. This results in inappropriate treatment of pregnant women. Use of drugs in pregnancy is not always wrong. For example, high fever is harmful for the fetus in the early months. Use of paracetamol is better than no treatment at all. Also, diabetes mellitus during pregnancy may need intensive therapy with insulin. Drugs have been classified into categories A,B,C,D and X based on the Food and Drug Administration(FDA) rating system to provide therapeutic guidance based on potential benefits and fetal risks. Drugs like multivitamins that have demonstrated no fetal risks after controlled studies in humans are classified as Category A. On the other hand drugs like thalidomide with proven fetal risks that outweigh all benefits are classified as Category X
Advice:
When you take your gestational diabetes test (around 24-28 weeks) cut back on your sugar/ carbs/ and fruit for like 3-5 days before. It will help get a more accurate reading and not a false positive- kwim? b/c going back for longer- when you shouldn’t have to sucks lol
Maybe check for anemia- BEFORE you are so far along??? They wait until about 3rd tri and I have a feeling I was before that- b/c I feel better on my supplements. Its not worth that feeling if I would have known. 1/3 of preggies are- so you might as well check sooner OR eat more Iron so its not a problem!
IF you have to take an Iron supplement- my Dr. recommends the brand “Slow- Fee” You can get it over the counter at any store- even Target. It release slower in your body and you don’t get the side affects. I like it much more then others I have taken in the past. Dont’ take 2 hours before or after you had Calcium. It also helps to take with Vitamin C so it gets absorbed better. This goes for taking Iron as in food too- your body absorbs Iron better without Calcium and caffine- which can block absorbtion. . . Iron is important for you and baby.
Pregnancy Tips , Pregnancy Tips Health, Pregnancy Tips Health Latest, Pregnancy Tips Health Information, Pregnancy Tips Health information, Pregnancy Tips Health Photo,Pregnancy Tips Health photo, Pregnancy Tips Health Latest, Pregnancy Tips Health latest, Pregnancy Tips Health Story, Healthy Minnesota Health story, Pregnancy Tips Video, Pregnancy Tips video, Pregnancy Tips Health History, Pregnancy Tips Health history, Pregnancy Tips over Picture, history, Pregnancy Tips Asia, Healthy Minnesota asia, Pregnancy Tips Gallery, Pregnancy Tips gallery, Pregnancy Tips Photo Gallery, Healthy Minnesota photo gallery, Pregnancy Tips Picture, Pregnancy Tips picture, Pregnancy Tips Web, Malaysia Health, web Health, picture, video photo, video surgery, gallery, laparoscopy, virus, flu, drug, video, Health Health, photo, nutrition, health video, symptoms, cancer, medical, diet, organic, weightloss, surgery, fitness, operation, bf1, pregnancy, obstetrics, pregnant, neonatal, gynecology, and, labor, delivery, tips, nurses, midwife, trimesters, OB