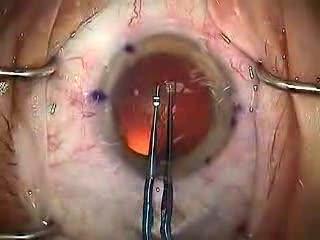
Modern Cataract Surgery
[media id=35 width=500 height=400]
Cataract surgery is the removal of the natural lens of the eye (also called “crystalline lens”) that has developed an opacification, which is referred to as a cataract. Metabolic changes of the crystalline lens fibers over the time lead to the development of the cataract and loss of transparency, causing impairment or loss of vision. During cataract surgery, a patient’s cloudy natural lens is removed and replaced with a synthetic lens to restore the lens’s transparency.
Following surgical removal of the natural lens, an artificial intraocular lens implant is inserted (eye surgeons say that the lens is “implanted”). Cataract surgery is generally performed by an ophthalmologist (eye surgeon) in an ambulatory (rather than inpatient) setting, in a surgical center or hospital, using local anesthesia (either topical, peribulbar, or retrobulbar), usually causing little or no discomfort to the patient. Well over 90% of operations are successful in restoring useful vision, with a low complication rate. Day care, high volume, minimally invasive, small incision phacoemulsification with quick post-op recovery has become the standard of care in cataract surgery all over the world.
Types of surgery
Extracapsular cataract extraction involves the removal of almost the entire natural lens while the elastic lens capsule (posterior capsule) is left intact to allow implantation of an intraocular lens. There are two main types of cataract surgery:
Phacoemulsification (Phaco) is the preferred method in most cases. It involves the use of a machine with an ultrasonic handpiece equipped with a titanium or steel tip. The tip vibrates at ultrasonic frequency (40,000 Hz) and the lens material is emulsified. A second fine instrument (sometimes called a cracker or chopper) may be used from a side port to facilitate cracking or chopping of the nucleus into smaller pieces. Fragmentation into smaller pieces makes emulsification easier, as well as the aspiration of cortical material (soft part of the lens around the nucleus). After phacoemulsification of the lens nucleus and cortical material is completed, a dual irrigation-aspiration (I-A) probe or a bimanual I-A system is used to aspirate out the remaining peripheral cortical material.
Conventional extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE): It involves manual expression of the lens through a large (usually 10–12 mm) incision made in the cornea or sclera. Although it requires a larger incision and the use of stitches, the conventional method may be indicated for patients with very hard cataracts or other situations in which phacoemulsification is problematic. Microincision cataract surgery involves a technique by which a cataract can be reached through an incision of 1.5 millimeters or less.
Cryoextraction is a form of ICCE that freezes the lens with a cryogenic substance such as liquid nitrogen[4]. In this technique, the cataract is extracted through use of a cryoextractor — a cryoprobe whose refrigerated tip adheres to and freezes tissue of the lens, permitting its removal. Although it is now used primarily for the removal of subluxated lenses, it was the favored form of cataract extraction from the late 1960s to the early 1980s
Intraocular lenses
Intraocular lens implantation: After the removal of the cataract, an intraocular lens (IOL) is usually implanted into the eye, either through a small incision (1.8 mm to 2.8 mm) using a foldable IOL, or through an enlarged incision, using a PMMA (polymethylmethacrylate) lens. The foldable IOL, made of silicone or acrylic material of appropriate power is folded either using a holder/folder, or a proprietary insertion device provided along with the IOL. The lens implanted is inserted through the incision into the capsular bag within the posterior chamber (in-the-bag implantation). Sometimes, a sulcus implantation (in front or on top of the capsular bag but behind the iris) may be required because of posterior capsular tears or because of zonulodialysis. Implantation of posterior-chamber IOL (PC-IOL) in patients below 1 to 2 years of age is relatively contraindicated due to rapid ocular growth at this age and the excessive amount of inflammation, which may be very difficult to control. Optical correction in these patients without intraocular lens (aphakic) is usually managed with either special contact lenses or glasses. Secondary implantation of IOL (placement of a lens implant as a second operation) may be considered after 2 years of age. New designs of multi-focal intra-ocular lens are now available. These lenses allow focusing of rays from distant as well as near objects, working much like bifocal or trifocal eyeglasses. Pre-operative patient selection and good counselling is extremely important to avoid unrealistic expectations and post-operative patient dissatisfaction. Acceptability for these lenses has become better and studies have shown good results in selected patients. Brands in the market include: ReSTOR (R), Rezoom (R) and Technis MF (R).
Preoperative evaluation
An eye examination or pre-operative evaluation by an eye surgeon is necessary to confirm the presence of a cataract and to determine if the patient is a suitable candidate for surgery. The patient must fulfill certain requirements such as:The degree of reduction of vision due, at least in large part, to the cataract should be evaluated. While the existence of other sight-threatening diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration or glaucoma, does not preclude cataract surgery, less improvement may be expected than in their absence.
The eyes should have a normal pressure, or any pre-existing glaucoma should be adequately controlled on medications. In cases of uncontrolled glaucoma, a combined cataract-glaucoma procedure (Phaco-trabeculectomy) can be planned and performed.
The pupil should be adequately dilated using eyedrops; if pharmacologic pupil dilation is inadequate, procedures for mechanical pupillary dilatation may be needed during the surgery.
Operation procedures
The surgical procedure in phacoemulsification for removal of cataract involves a number of steps. Each step must be carefully and skillfully performed in order to achieve the desired result. The steps may be described as follows:
Anaesthesia,
Exposure of the eyeball using a lid speculum,
Entry into the eye through a minimal incision (corneal or scleral)
Viscoelastic injection to stabilize the anterior chamber and to help maintain the eye pressurization
Capsulorhexis
Hydrodissection pie
Hydro-delineation
Ultrasonic destruction or emulsification of the cataract after nuclear cracking or chopping (if needed), cortical aspiration of the remanescent lens, capsular polishing (if needed)
Implantation of the artificial IOL
Entration of IOL (usually foldable)
Viscoelastic removal
Wound sealing / hydration (if needed).
The pupil is dilated using drops (if the IOL is to be placed behind the iris) to help better visualise the cataract. Pupil constricting drops are reserved for secondary implantation of the IOL in front of the iris (if the cataract has already been removed without primary IOL implantation). Anesthesia may be placed topically (eyedrops) or via injection next to (peribulbar) or behind (retrobulbar) the eye. Oral or intravenous sedation may also be used to reduce anxiety. General anesthesia is rarely necessary, but may be employed for children and adults with particular medical or psychiatric issues. The operation may occur on a stretcher or a reclining examination chair. The eyelids and surrounding skin will be swabbed with disinfectant. The face is covered with a cloth or sheet, with an opening for the operative eye. The eyelid is held open with a speculum to minimize blinking during surgery. Pain is usually minimal in properly anesthetised eyes, though a pressure sensation and discomfort from the bright operating microscope light is common. The ocular surface is kept moist using sterile saline eyedrops or methylcellulose viscoelatic. The discission into the lens of the eye is performed at or near where the cornea and sclera meet (limbus = corneoscleral junction). Advantages of the smaller incision include use of few or no stitches and shortened recovery time. . A capsulotomy (rarely known as cystotomy) is a procedure to open a portion of the lens capsule, using an instrument called a cystotome. An anterior capsulotomy refers to the opening of the front portion of the lens capsule, whereas a posterior capsulotomy refers to the opening of the back portion of the lens capsule. In phacoemulsification, the surgeon performs an anterior continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis, to create a round and smooth opening through which the lens nucleus can be emulsified and the intraocular lens implant inserted.
Complications
Complications after cataract surgery are relatively uncommon.
Some people can develop a posterior capsular opacification (also called an after-cataract). As a physiological change expected after cataract surgery, the posterior capsular cells undergo hyperplasia and cellular migration, showing up as a thickening, opacification and clouding of the posterior lens capsule (which is left behind when the cataract was removed, for placement of the IOL). This may compromise visual acuity and the ophthalmologist can use a device to correct this situation. It can be safely and painlessly corrected using a laser device to make small holes in the posterior lens capsule of the crystalline. It usually is a quick outpatient procedure that uses a Nd-YAG laserposterior capsulotomy). This creates a clear central visual axis for improving visual acuity. . In very thick opacified posterior capsules, a surgical (manual) capsulectomy is the surgical procedure performed. (neodymium-yttrium-aluminum-garnet) to disrupt and clear the central portion of the opacified posterior lens capsule (
Posterior capsular tear may be a complication during cataract surgery. The rate of posterior capsular tear among skilled surgeons is around 2% to 5%. It refers to a rupture of the posterior capsule of the natural lens. Surgical management may involve anterior vitrectomy and, occasionally, alternative planning for implanting the intraocular lens, either in the ciliary sulcus, in the anterior chamber (in front of the iris), or, less commonly, sutured to the sclera.
Retinal detachment is an uncommon complication of cataract surgery, which may occur weeks, months, or even years later.
Toxic Anterior Segment Syndrome or TASS is a non-infectious inflammatory condition that may occur following cataract surgery. It is usually treated with topical corticosteroids in high dosage and frequency.
Cataract Surgery , Cataract Surgery Health, Cataract Surgery Health Latest, Cataract Surgery Health Information, Cataract Surgery Health information, Cataract Surgery Health Photo,Exercising for Weight Health photo, Cataract Surgery Health Latest, Cataract Surgery Health latest, Exercising for Weight Health Story, Healthy Minnesota Health story, Cataract Surgery Video, Cataract Surgery video, Cataract Surgery Health History, Cataract Surgery Health history, Cataract Surgery over Picture, history, Cataract Surgery Asia, Healthy Minnesota asia, Cataract Surgery Gallery, Exercising for Weight gallery, Cataract Surgery Photo Gallery, Healthy Minnesota photo gallery, Cataract Surgery Picture, Cataract Surgery picture, Cataract Surgery Web, Malaysia Health, web Health, picture, video photo, video surgery, gallery, laparoscopy, virus, flu, drug, video, Health Health, calories, photo, nutrition, health video, symptoms, cancer, medical, beating, diet, organic, blister, exercise, weightloss, surgery, spiritual, eating, tips, skin, operation, bf1, cataract, surgery, phaco, eye, resident, education




