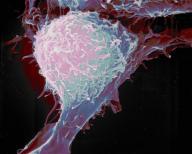
Prostate cancer screening: More harm than good?
One meaning of screening is the investigation of a great number of something (for instance, people) looking for those with a particular problem or feature. For example at an airport many bags are screened by x-ray to try to detect any which may contain weapons or explosives, and people are screened by passing through a metal detector. If only part of a population is screened, screening is equivalent to sampling in statistics.
Screening can also mean preventing access of something by some sort of barrier. Particular cases:
Electromagnetic shielding in physics, the exclusion of electric, magnetic, or electromagnetic fields by a metallic screen or shield
In atomic physics and chemistry, the screening effect or atomic shielding is the reduction of effective nuclearcharge by intervening electron shells
Screening (printing), a process that represents lighter shades as tiny dots, rather than solid areas, of ink by passing ink through a perforated screen
The investigation of a large population is related; the members of a population are filtered by a metaphorical, rather than physical, screen
Screening is a process stage when cleaning paper pulp
Routine screening for prostate cancer has resulted in more than 1 million U.S. men being diagnosed with tumors who might otherwise have suffered no ill effects from them, U.S. researchers said on Monday.
They said prostate cancer screening is a double-edged sword, catching serious cancers in a few but causing needless worry and expense for the majority of men, who may be getting treatment for tumors growing too slowly to do any harm.
The team looked to see how many additional men have been diagnosed with prostate cancer since the introduction in 1986 of a widely used blood test for prostate cancer that looked for a prostate-cancer specific antigen, or PSA.
“Our estimate is that number is about 1.3 million people in the United States. That is a huge effect,” said Dr. H. Gilbert Welch of the VA Outcomes Group in White River Junction, Vermont, whose study appears in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
More than 1 million of those were treated, they found.
“These are men who could not be helped by treatment because their cancer was not destined to cause them symptoms or death,” Welch said in a telephone interview.
The increased diagnosis rate more than tripled in men aged 50 to 59 and increased more than a sevenfold in men under age 50.
And while prostate cancer deaths have declined since the introduction of PSA testing, Welch said about 20 men had to be diagnosed and treated for every one who benefited.
Prostate cancer , Prostate cancer Health, Prostate cancer Health Latest, Prostate cancer Health Information, Prostate cancer Health information, Prostate cancer Health Photo,Exercising for Weight Health photo, Prostate cancer Health Latest, Prostate cancer Health latest, Exercising for Weight Health Story, Healthy Minnesota Health story, Prostate cancer Video, Prostate cancer video, Prostate cancer Health History, Prostate cancer Health history, Prostate cancer over Picture, history, Prostate cancer Asia, Healthy Minnesota asia, Prostate cancer Gallery, Exercising for Weight gallery, Prostate cancer Photo Gallery, Healthy Minnesota photo gallery, Prostate cancer Picture, Prostate cancer picture, Prostate cancer Web, Malaysia Health, web Health, picture, video photo, video surgery, gallery, laparoscopy, virus, flu, drug, video, Health Health, calories, photo, nutrition, health video, symptoms, cancer, medical, beating, diet, organic, blister, exercise, weightloss, surgery, spiritual, eating, tips, skin, operation, bf1, Prostate, cancer, screening




