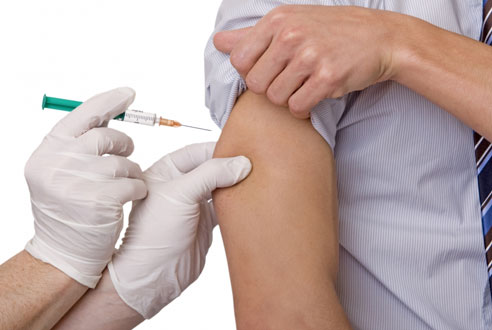
 Four years ago at age 78, R., a retired professional known as much for her small-town Minnesotan resilience as her commitment to public service, developed a fleeting rash over her left chest. The rash, which turned out to be shingles, or herpes zoster, was hardly noticeable.
Four years ago at age 78, R., a retired professional known as much for her small-town Minnesotan resilience as her commitment to public service, developed a fleeting rash over her left chest. The rash, which turned out to be shingles, or herpes zoster, was hardly noticeable.
But the complications were unforgettable.
For close to a year afterward, R. wrestled with the searing and relentless pain in the area where the rash had been. “It was ghastly, the worst possible pain anyone could have,” R. said recently, recalling the sleepless nights and fruitless search for relief. “I’ve had babies and that hurts a lot, but at least it goes away. This pain never let up. I felt like I was losing my mind for just a few minutes of peace.”
Shingles and its painful complication, called postherpetic neuralgia, result from reactivation of the chicken pox virus, which remains in the body after a childhood bout and is usually dormant in the adult. Up to a third of all adults who have had chicken pox will eventually develop one or both of these conditions, becoming debilitated for anywhere from a week to several years. That percentage translates into about one million Americans affected each year, with older adults, whose immune systems are less robust, being most vulnerable. Once the rash and its painful sequel appear, treatment options are limited at best and carry their own set of complications.
While the search for relief costs Americans over $500 million each year, the worst news until recently has been that shingles and its painful complication could happen to any one of us. There were no preventive measures available.
But in 2006, the Food and Drug Administration approved a new vaccine against shingles. Clinical trials on the vaccine revealed that it could, with relatively few side effects, reduce the risk of developing shingles by more than half and the risk of post-herpetic neuralgia by over two-thirds. In 2008, a national panel of experts on immunizations at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention went on to recommend the vaccine to all adults age 60 and older.
At the time, the shingles vaccine seemed to embody the best of medicine, both old school and new. Its advent was contemporary medicine’s elegant response to a once intractable, age-old problem. It didn’t necessarily put an end to the spread of disease, in this case chicken pox; but it dramatically reduced the burden of illness for the affected individual. And, most notably, its utter simplicity was a metaphoric shot-in-the-arm for old-fashioned doctoring values. Among the increasingly complex and convoluted suggestions for health care reform that were brewing at that moment, here was a powerful intervention that relied on only three things: a needle, a syringe and a patient-doctor relationship rooted in promoting wellness.
Not.
In the two years since the vaccine became available, fewer than 10 percent of all eligible patients have received it. Despite the best intentions of patients and doctors (and no shortage of needles and syringes), the shingles vaccine has failed to take hold, in large part because of the most modern of obstacles. What should have been a widely successful and simple wellness intervention between doctors and their patients became a 21st century Rube Goldberg-esque nightmare.
Last month in The Annals of Internal Medicine, researchers from the University of Colorado in Denver and the C.D.C. surveyed almost 600 primary care physicians and found that fewer than half strongly recommended the shingles vaccine. Doctors were not worried about safety — a report in the same issue of the journal confirmed that the vaccine has few side effects; rather, they were concerned about patient cost.
Although only one dose is required, the vaccination costs $160 to $195 per dose, 10 times more than other commonly prescribed adult vaccines; and insurance carriers vary in the amount they will cover. Thus, while the overwhelming majority of doctors in the study did not hesitate to strongly recommend immunizations against influenza and pneumonia, they could not do the same with the shingles vaccine.
“It’s just a shot, not a pap smear or a colonoscopy,” said Dr. Laura P. Hurley, lead author and assistant professor of medicine at the University of Colorado in Denver. “But the fact is that it is an expensive burden for all patients, even those with private insurance and Medicare because it is not always fully reimbursed.”
Moreover, many private insurers require patients to pay out of pocket first and apply for reimbursement afterward. And because the shingles vaccine is the only vaccine more commonly given to seniors that has been treated as a prescription drug, eligible Medicare patients must also first pay out of pocket then submit the necessary paperwork in order to receive the vaccine in their doctor’s office. It’s a complicated reimbursement process that stands in stark contrast to the automatic, seamless and fully covered one that Medicare has for flu and pneumonia vaccines.
Despite this payment maze, some physicians have tried to stock and administer the vaccine in their offices; many, however, eventually stop because they can no longer afford to provide the immunizations. “If you have one out of 10 people who doesn’t pay for the vaccine, your office loses money,” said Dr. Allan Crimm, the managing partner of Ninth Street Internal Medicine, a primary care practice in Philadelphia. Over time, Dr. Crimm’s practice lost thousands of dollars on the shingles vaccine. “It’s indicative of how there are perverse incentives that make it difficult to accomplish what everybody agrees should happen.”
Even bypassing direct reimbursement is fraught with complications for doctors and patients. A third of the physicians surveyed in the University of Colorado study resorted to “brown bagging,” a term more frequently used to describe insurers who have patients carry chemotherapy drugs from a cheaper supplier to their oncologists’ offices. In the case of the shingles vaccine, the study doctors began writing prescriptions for patients to pick up the vaccine at the pharmacy and then return to have it administered in their offices. However, the shingles vaccine must be frozen until a few minutes before administration, and a transit time greater than 30 minutes between office and pharmacy can diminish the vaccine’s effectiveness.
Dr. Crimm and the physicians in his office finally resorted to what another third of the physicians in the study did: they gave patients prescriptions to have the vaccine administered at pharmacies that offered immunization clinics. But when faced with the added hassles of taking additional time off from work and making a separate trip to the pharmacy, not all patients followed through. “Probably about 60 percent of our patients finally did get the vaccine at the pharmacy,” Dr. Crimm estimated. “This is as opposed to 98 percent of our patients getting the pneumonia and influenza vaccines, immunizations where they just have to go down the hall because we stock it, roll up their sleeves then walk out the door.”
With all of these barriers, it comes as no surprise that in the end only 2 percent to 7 percent of patients are immunized against shingles. “There’s just so much that primary care practices must take care of with chronic diseases like obesity and diabetes and heart disease,” Dr. Hurley noted. “If a treatment isn’t easy to administer, then sometimes it just falls to the bottom of the list of things for people to do.”
“Shingles vaccination has become a disparity issue,” Dr. Hurley added. “It’s great that this vaccine was developed and could potentially prevent a very severe disease. But we have to have a reimbursement process that coincides with these interventions. Just making these vaccines doesn’t mean that they will have a public health impact.”


 U.S. Marine Lance Cpl. Greg Rivers, 20, of Sylvester, Ga., waits to take psychological tests at the Marine Corps Air Ground Combat Center in Twentynine Palms, Calif. on Sept. 29, 2009.
U.S. Marine Lance Cpl. Greg Rivers, 20, of Sylvester, Ga., waits to take psychological tests at the Marine Corps Air Ground Combat Center in Twentynine Palms, Calif. on Sept. 29, 2009.