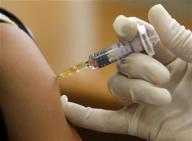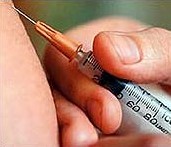
Thailand wins praise for AIDS vaccine trial
An experimental AIDS vaccine that appears to be the first to protect people was mired for years in controversy, and credit for its success must go to Thailand where the trial was conducted, experts said.
The trial was criticised five years ago by 22 prominent U.S. scientists who doubted it would have any effect. Washington was accused of wasting more than a $100 million by funding it.
But Thai health authorities and their U.S. partners at the National Institutes of Health and the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research pressed on with the trial involving 16,000 volunteers in a country at the forefront of the battle against HIV.
“It was a tough decision. I am glad we made it,” said Dr. Anthony Fauci, director of the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, who defied the criticism and continued the trial.
The trial vaccine was made using two failed products — Sanofi-Pasteur’s ALVAC canary pox/HIV vaccine and AIDSVAX, made by a San Francisco company called VaxGen and now owned by the non-profit Global Solutions for Infectious Disease.
Donald Burke, dean of the University of Pittsburgh’s Graduate School of Public Health, said the trial was controversial from the start and had been dismissed by prominent U.S. scientists because of the failure of previous vaccine tests.
“But given the importance of the AIDS epidemic, the decision was made to go forward regardless of these criticisms. It was a difficult choice, but a courageous choice,” said Burke, who was head of AIDS research at Walter Reed before retiring in 1997.
Burke isolated the AIDS virus taken from a young HIV-infected Thai soldier in 1989 after Thai army doctors discovered an HIV outbreak among young recruits in Chiang Mai in northern Thailand. That virus sample went on to become one of the seed viruses in the experimental vaccine, Burke said.
To their credit the Thais did a remarkable job on this,” Dr. Eric Schoomaker, the Surgeon General of the U.S. Army, told reporters. “They did remarkable job of recruiting volunteers and conducting this trial almost flawlessly.”
The $105 million trial was sponsored and paid for by the U.S. government and results showed it cut the risk of infection by 31.2 percent among 16,402 volunteers over three years.
THAI TRIUMPH
Those results mark a triumph for Thailand, a country of 67 million people where a booming sex industry had stoked fears of a major epidemic. Local authorities battled hard against a disease that threatened to spiral out of control some 20 years ago.
Experts had predicted that 4 million people would be infected by 2000 if nothing was done to slow the spread of HIV. But a massive government-led Aids education and prevention campaign in the early 1990s had an enormous effect.
HIV prevalence among injecting drug users in Thailand was as high as 30-50 percent in 1991, and 33.2 percent among female sex workers in 1994, according to UNAIDS. The number of infections has since been reduced to 20,000 annually from 140,000 in 1991.
Billboards and airwaves were bombarded with safe sex messages while health workers promoted condom use in the country’s notorious sex trade. Leading the campaign was “Mr Condom,” family planner-turned Public Health Minister, Meechai Viravaidya.
Health check-ups were made available to sex workers for free. Men were discouraged from visiting prostitutes and condom usage in Bangkok’s brothels rose from 15 percent in the early 1990s to 98 percent by 2000.
Infection rates fell and the exercise remains widely cited as a model in disease prevention among health experts — although numbers have shown signs of creeping up in the last few years among some high risk groups, such as gay and bisexual men.
Thailand wins praise, Thailand wins praise Health, Thailand wins praise Health Latest, Thailand wins praise Health Information, Thailand wins praise Health information, Thailand wins praiseHealth Photo,Thailand wins praise for Weight Health photo, Thailand wins praise Health Latest, Thailand wins praiseHealth latest, Thailand wins praise for Weight Health Story, Healthy Minnesota Health story, Thailand wins praise Video, Thailand wins praise video, Thailand wins praise Health History, Thailand wins praise Health history, Thailand wins praiseover Picture, history, Thailand wins praise Asia, Healthy Minnesota asia, Thailand wins praise Gallery, Thailand wins praise for Weight gallery, Thailand wins praise Photo Gallery, Healthy Minnesota photo gallery, Thailand wins praise Picture, Thailand wins praise picture, Thailand wins praise Web, Malaysia Health, web Health, web Health picture, video photo, video surgery, gallery, laparoscopy, virus, flu, drug, video, Health Health, calories, photo, nutrition, health video, symptoms, cancer, medical, beating, diet, physical, Training, organic, gym, blister, exercise, weightloss, surgery, spiritual, eating, tips, skin, operation, bf1, Thailand, wins, praise,for, AIDS, vaccine, trial